Current Internet Usage Statistics
Global Internet Users in 2024
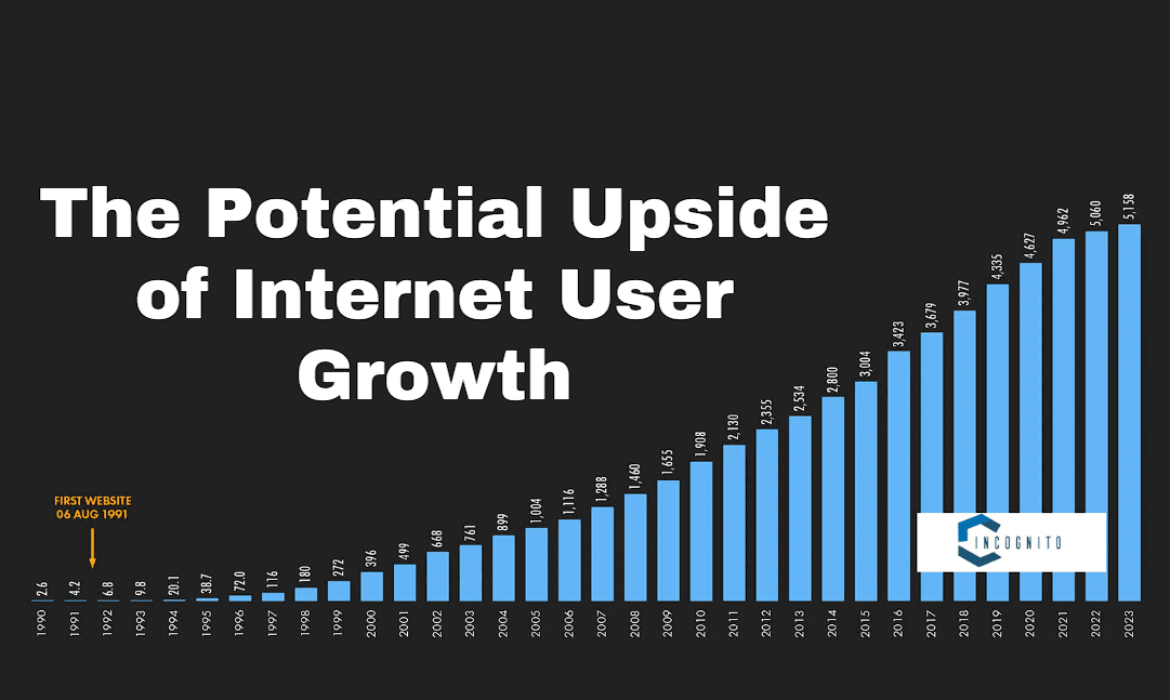
As of April 2024, there are about 5.44 billion internet users in the world, equating to 67.1 percent of the earth’s population. The stated figure is a topmost remarkable achievement with a year-on-year increase of 178 million users. With a growth rate of 3.4 percent, the above graph portrays the growth line in expanding internet access around the globe. The continuous increment of users clearly shows an upward trajectory in the penetration of digital technologies.
Expected Growth in 2029
Projections put the number of Internet users at 7.9 billion by 2029. That is a 47% rise from the figures of today. Given the growth rate that is projected, it would be expected to be practically universal internet adoption as more and more regions will possess the necessary infrastructure. The projection also demonstrates the increasing pace of digital integration into life, powered by improvements in technology and the falling cost of internet access.
Daily Basis Usage Patterns of the Internet
People consume an average of the internet for a total of 6 hours and 35 minutes daily. This figure has been pretty steady for the last year, proving that the internet is as relevant as ever to daily routines.
The huge usage per day further supports the fact that the internet acts as one of the core sources of information, entertainment, and communication today. With the development of such habits, a very interesting and extremely pertinent story unfolds before businesses, governments, and people in general, while the Internet continues to shape life as we know it today.
Demographics and Access
Youth vs. Adult Internet Access

The digital divide between the young and the old is also very wide. Seventy-five percent of people aged between 15 through 24 years are internet users, while only 65% of those aged 25 years and above are connected to the information superhighway. This also means that the younger generation has the upper edge to access the internet, besides being digital natives.
They have tended to spend their childhood years growing up with digital technologies as an effortless routine and, for this reason, are more likely to be both interested in and able to while away their time seeking out access as well as how it is used. This generational divide in internet usage bodes implications for school, work, and social life, more so, when young users take center stage as the internet driving force.
Use of the Internet via Mobile
Percentage-wise, 96.3 of the surveyed internet users use, or rather, access, to the internet through mobile devices. In terms of time, 57.8 percent of time spent online is on mobile, mainly because of sustaining a lifeline monopoly on the broadband connection.
This trend is particularly important in areas where fixed broadband infrastructure is not available, while conversely, mobile networks are widespread. The dominance of mobile internet use also begins to have a bearing on how digital content and services are designed to reach and appeal to the requirements of mobile users.
Regional Inequities in Internet Access
Despite the growth in accessibility globally, Internet penetration still suffers from major regional imbalances. For example, China, has the highest number of internet users in the world, up to 77.5% of the population.
For instance, in contrast, some regions of Africa have a bare majority, which is still grappling with low internet connectivity and weak infrastructure widespread. These disparities underscore the problems on the way to global digital equality. Resolving these issues will be crucial in allowing internet growth to benefit all regions more equitably.
Social Media Growth
Growth of Social Media Users in 2024
In the year 2024, the number of people using social media population rise to about 5.04 billion in the world. The numerical figure makes up 62.6% of the world’s population. These informed individuals say that the growth experienced in this sector directly relates to spicy internet access rates, especially in the developing world, where people start their digital engagement with their social media accounts. The social media users’ growth rate is a mirror of human activity trends since most have now become inalienable in providing essential communication and social networking functions.
Content Creation on the Internet
There are 7.5 million blog posts on the Internet boasting every day. This huge content generation is a clear sign of the important role the Internet has to play in assisting people and circulating information.
Blogs, social media posts, and other user-generated content will help cast some light on just how rich and diverse the information available on the Internet is to assist people and organizations to be able to telling their own stories, convey ideas, and offer expert knowledge to the global audience. The volume of content generated each day further proves that the internet plays its role as a fluid and ever-evolving communication medium.
Contribution to Economic Growth
Impact on growth in GDP
The internet has played a great role in contributing to the growth in GDP in the world. The Internet contributed to approximately 21% of the amount of GDP growth in the past five years. The internet, in the most extensive economies, creates approximately 3.4 percent in the way of GDP, thereby proving to be contributing to the growth of a country.
Developing economies benefit, but not as much as developed regions used; the Internet adds practically half to the GDP growth. This may mean that the digital infrastructure and the level of penetration of the Internet in these regions are different, and this being at variance then causes a difference in the impact.
Connectivity and GDP Growth
From research, it is apparent that a 10% increase in internet access can yield a surge in global GDP growth to approximately 1.38%. The increase of 10% in the OECD can yield as much as 2% in GDP growth to new peaks.
It is a fact that these improvements do bear substantial economic benefits, especially in the low-internet connectivity geographies. The increase in connectivity uplifts economic productivity, opens fresh markets, and essentially imbibes innovation.
Business Transformation
Productivity Gains Across Sectors
In many ways, internet use has meant more productivity across many firms and businesses. In a study that surveyed firms from across the globe, internet usage raised productivity, even in environments dogged by challenges such as corruption or underdeveloped financial markets.
For instance, in manufacturing, the use of internet-linked gadgets means fewer operations, lowered downtime, and resultant supply chain efficiency. Online service platforms make it possible for firms to reach more consumers while promoting sales and engagement with compared consumers.
Empowering Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Internet access has indeed empowered Small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The internet contributes around 75% of its economic impact to traditional companies, not firms working purely online. The digital tools used by SMEs are to handle the essential supply chain, customer involvement, and marketing in novel ways.
In the case of an SME in the retail category, it can easily reach customers globally by the use of e-commerce platforms without the need for a physical storefront. This global market access has changed the business scenario and has opened doors for SMEs towards having competitions with some of the big companies.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Catalyst for Startups and New Business Models
The open nature of the Internet encourages innovation and entrepreneurship. It permits the development of new business models, for example, the e-commerce and sharing economy business models. For example, mobile technologies have eased the provision of financial services in developing regions.
The M-PESA system in Kenya enables subscribers to transact money using their mobile phones. This has significantly changed the attitude and perception of financial inclusion in regions that have previously been perceived to have low penetration in the conventional banking model.
Job Creation and Economic Opportunities
The internet creates new job opportunities both within the tech ecosystem and beyond. Automation and digitalization indeed remove some tasks and jobs, but their net impact is positive for job creation in a huge part of the economy, particularly in sectors dynamic in the adaptation to digital transformations.
For example, the growth of the internet, and especially e-commerce, has expanded the demand for positions in logistics, customer service, and IT support. These new jobs have offset job losses in traditional retail and clearly highlight the power of the Internet to transform labor markets.
Social and Economic Development
Better Standard of Life
Strong correlations exist between internet maturity and increasing living standards. An increase in internet penetration correlates with a higher per capita GDP, and estimates suggest an average increase of $500 in real per capita GDP with advancement in internet infrastructure.
This underlines the means by which the internet grows economic opportunity and makes life better for more people. It is in the realization that internet maturity affords these excellent opportunities and uplifts communities in remote and underserved areas in terms of online education and remote work opportunities.
Dealing with Global Disparities
In general, almost every country is doing well in the growth of the internet sector, with much dissimilarity in the regions as well as the distribution of the economic benefits. Globally, the internet landscape is contributing to growth in many countries, including strong internet ecosystems in the United States, China, and India, supported by rapid economic growth through digital innovation.
In this sector, milestone development is significantly low in many developing countries due to low connectivity and also being characterized by inferior infrastructure. More importantly, addressing such disparities is key to ensuring that the benefits of this kind of development spurred by the internet are shared on a global scale.
This will require agenda-based investments on the ground and in the digital infrastructure of least-served regions to flatten the disparities and promote opportunities for growth equitably.



