Understanding the world of investing can be like navigating a labyrinth, but the benefits are immense. From stocks to bonds, each investment type offers unique opportunities to grow your wealth. In this article, we will dive into the essentials of various investment options, spotlighting their potential returns and risks. Get ready to uncover the strategies that can lead you to financial success and stability. Enhance your trading techniques by learning from professionals. More Information is on the official website of Immediate Mator, a link between investors and education firms.
Simple Moving Average (SMA) Crossover Strategy
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) Crossover Strategy is a widely used technique in technical analysis that involves two SMAs of different lengths to identify potential trading signals. An SMA is calculated by taking the average of a security’s price over a specified number of periods. The strategy typically involves a shorter-term SMA and a longer-term SMA. For example, traders might use a 50-day SMA and a 200-day SMA.
The core of the SMA crossover strategy is to generate buy or sell signals based on the crossovers of these two SMAs. A buy signal occurs when the shorter-term SMA crosses above the longer-term SMA, indicating a potential uptrend. Conversely, a sell signal is generated when the shorter-term SMA crosses below the longer-term SMA, suggesting a potential downtrend. This crossover provides traders with an indication of shifting momentum and trend direction.
The SMA crossover strategy is appreciated for its simplicity and ease of use. However, it also has limitations, such as lagging signals due to the averaging process, which may result in delayed entry or exit points. Additionally, during periods of low volatility or sideways market conditions, the SMA crossover strategy may produce false signals or whipsaws, making it essential for traders to use additional confirmation tools and risk management techniques.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) Crossover Strategy
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) Crossover Strategy is another popular trading approach that utilizes two EMAs of different lengths to generate trading signals. Unlike the SMA, the EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to recent price movements and potentially more useful for capturing short-term trends.
In this strategy, traders use a short-term EMA and a long-term EMA, such as the 12-day EMA and the 26-day EMA. Buy signals occur when the short-term EMA crosses above the long-term EMA, suggesting a bullish trend. Conversely, sell signals are generated when the short-term EMA crosses below the long-term EMA, indicating a bearish trend. The EMA crossover strategy is often favored for its quicker reaction to price changes compared to the SMA crossover.
While the EMA crossover strategy can provide timely signals, it is not without drawbacks. The sensitivity of the EMA to recent price changes can lead to false signals during choppy or consolidating market conditions. Traders may need to complement the EMA crossover with additional indicators or filters to enhance signal accuracy and reduce the likelihood of whipsaws.
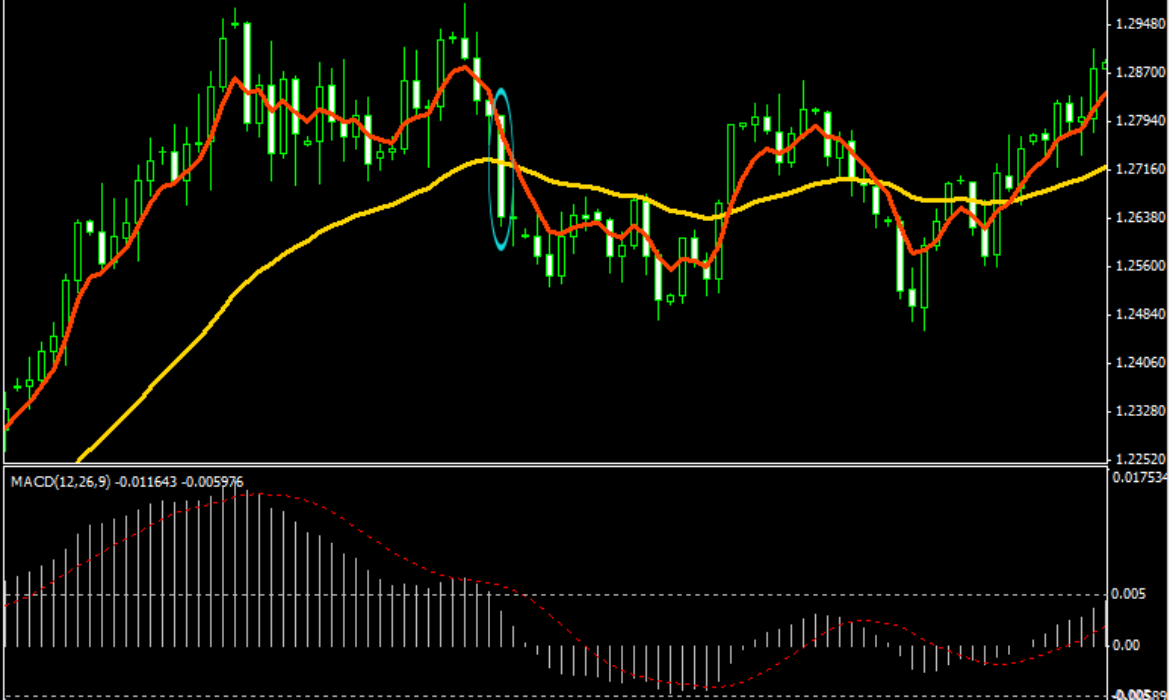
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) Crossover Strategy
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) Crossover Strategy is a well-known momentum-based trading strategy that combines multiple moving averages to identify potential trend reversals and trading opportunities. The MACD is calculated by subtracting the 26-day EMA from the 12-day EMA, resulting in the MACD line. A 9-day EMA of the MACD line, known as the signal line, is also plotted to generate trading signals.
The core of the MACD crossover strategy lies in the interaction between the MACD line and the signal line. A buy signal is generated when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, indicating a potential bullish trend. Conversely, a sell signal occurs when the MACD line crosses below the signal line, suggesting a potential bearish trend. Additionally, traders often monitor the MACD histogram, which represents the difference between the MACD line and the signal line, for additional confirmation and trend strength.
The MACD crossover strategy is valued for its ability to provide clear signals and its versatility across different time frames and markets. However, it may produce lagging signals, as the MACD is based on moving averages, which are inherently reactive. To address this, traders may use the MACD crossover in conjunction with other technical indicators and market analysis tools to improve signal accuracy and manage risk effectively.
Conclusion
Investing wisely can be your ticket to financial freedom and security. By exploring diverse options and understanding their nuances, you set yourself up for long-term success. Remember, every investment comes with its own set of risks and rewards, and making informed choices is key. Stay vigilant, keep learning, and continuously refine your strategy. With the right approach, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the investment landscape and achieve your financial goals. Your journey to financial empowerment starts here—embrace it with confidence and curiosity.



