
In markets with a high degree of commoditization, digital transformation activities and strategies are frequently more urgent and present. At this point, it’s not so much a question of companies deciding to convert as it is of deciding how to transform.
This digital transformation guide will tell you the importance and definition of digital transformation. We will also list down the pillars of the same for giving a better insight.
What Is Digital Transformation (Overall)?
The process of leveraging digital technology to develop new or change current business processes, culture, and customer experiences to suit changing business and market requirements is known as digital transformation. Digital transformation is the rethinking of business in the digital era.
It extends beyond typical responsibilities like sales, marketing, and customer support. Instead, digital transformation begins and ends with how you perceive and interact with consumers. With digital technology on our site, we have the opportunity to reinvent how we conduct business, and how we engage our customers as we go from paper to spreadsheets to smart applications for business management.
There is no need for small firms who are just getting started to build up their business procedures and then alter them afterwards. You can foresee the destiny of your organisation from the start. Building a 21st-century firm on sticky notes and handwritten ledgers is just not feasible.
Digital thinking, planning, and building positions you to be nimble, adaptable, and ready to expand. Many businesses are taking a step back as they begin on digital transformation to assess if they are doing the right things.
So, this is the definition of digital transformation.
What Is Digital Transformation In Manufacturing?
The next section in our digital transformation guide is related to manufacturing. The use of digital technologies to replace traditional or non-digital manufacturing and near-manufacturing processes and activities to improve company performance is referred to as digital transformation in manufacturing.
This smart, technology-driven manufacturing approach enables businesses to make the most of industrial solutions and adapt production in real-time to changing conditions and requirements, streamline processes, improve management and internal workflows, optimise production, or transform any other aspect of your manufacturing business.
This industry disposes of a large number of physical assets (from the manufacturing floor to the supply chain, back office, IT infrastructure, and so on) and recovers massive volumes of data. The objective of digital solutions in this context is to integrate assets and data in such a way that they provide value to every operation and process.
Industry 4.0 is the current industrial revolution at the centre of digital transformation in production, automating processes and enabling real-time control. This is made feasible by relying on efficient technologies that integrate assets and data, as well as combining digital and traditional manufacturing to get the greatest outcomes.
What Is Digital Transformation In Healthcare?
The health care sector is confronting the third evolutionary wave of IT digital technologies, which has such far-reaching consequences that analysts think it heralds a new era of global computing. Indeed, basic technologies such as mobility, Internet of Things (IoT), Web 3.0, PaaS/SaaS, Big Data, and Unified Communications will catalyse digital transformation in all businesses (UC).
A “digital thread” will unleash a continuous flow of data spanning from health care records and systems to patients interacting with care teams at any time and from any location during the next ten years. With the Internet becoming the pillar of our modern economy and mobile usage increasing at an exponential rate, all industries, including health care, are poised to benefit from the ubiquitous and real-time access to contextual information enabled by the new technologies driving the digital transformation narrative.
What are the benefits of digital transformation? It has the potential to revolutionise operations, lower costs, and improve the quality of patient services and care. Health-care companies that leverage mobility, Big Data, UC, and IoT will improve the whole healthcare service delivery chain, from diagnosis to post-care, while also enhancing relationships with patients, caregivers, and other leveraged partners.
Automated, efficient, and mobile processes will be implemented. The industry’s value chain is shifting from reliance on physical assets to reliance on digital assets, and the impact in the future will be more significant and opportunities than ever before.
Why Digital Transformation Is Important?
While each digital transformation specialist effort will have its unique set of objectives, the overall goal of any digital transformation is to enhance your present operations. Companies must develop to remain competitive in their sector, which necessitates digital transformation. You will lag if you do not evolve.
According to Bain & Company research, “just 8% of worldwide firms have been able to achieve their desired business outcomes from their digital technology expenditures.” One of the tactics that distinguish leaders is that they invest more in transforming their businesses rather than just operating them.
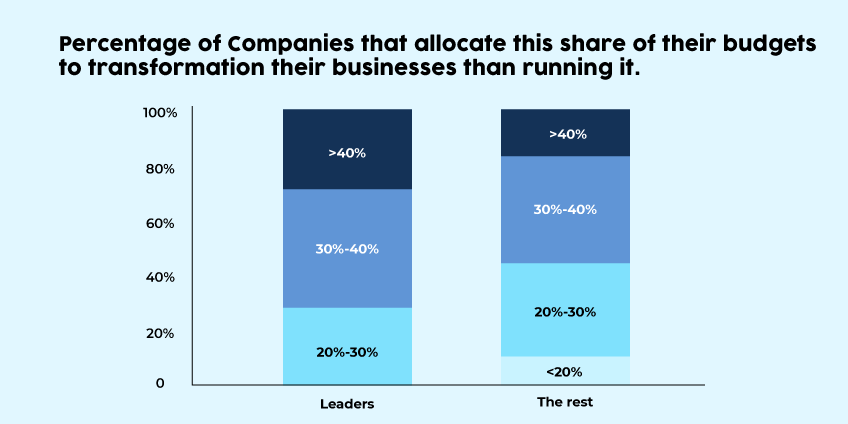
Digital transformation of industries is critical because it enables companies to adapt to ever-changing sectors and continuously enhance their operations. While the ROI of digital transformation is dependent on several things, the proper technology may significantly enhance how your organisation operates and how consumers interact with it.
-
Improves Productivity & Lowers Down The Labour Expenses
Using digital technology transformation to improve efficiency is one of the most powerful methods to alter your company. For example, for businesses, the time and money spent on training new staff and upgrading digital resources may soon add up. With the right tools, you can keep expenses down while increasing production.
-
Enhances Client Satisfaction
Tech-savvy customers want a fantastic experience across many touchpoints, such as mobile applications, social media, email, live chat, and so on. Improved consumer experiences are being driven by digital changes.
-
Increases The Competency Of The Brand
Whether you are interested in digital technology transformation or not, your rivals are. Choosing to ignore digital transformation is simply deciding that you don’t mind falling behind.
Major Pillars Of Digital Transformation Process
The main question that arises is what are the 4 main areas of digital transformation? We will outline everything related to the pillars of digital transformation program in the following section:
-
Technology
The sheer potential of new technologies is mind-boggling, ranging from the Internet of Things to blockchain, data lakes, and artificial intelligence. While many of them are becoming more user-friendly, understanding how a particular technology contributes to transformative opportunity, customising that technology to the unique needs of the organisation, and integrating it with current systems is highly difficult.
To make matters worse, most businesses have massive technical debt – entrenched old systems that are difficult to alter. Only professionals with technological depth and breadth, as well as the capacity to collaborate with the company, can address these problems. As challenging as these challenges are, an even more pressing issue is that many business executives have lost trust in their IT department’s capacity to drive substantial change, as many IT departments are solely concerned with “keeping the lights on.”
However, because digital transformation must eventually include institutional IT, confidence must be rebuilt. This implies that with each technological breakthrough, developers must give and demonstrate commercial benefits. As a result, executives in the technology sector must be excellent communicators with the strategic acumen to make technological decisions that balance innovation and dealing with technical debt.
-
Data
Unfortunately, most data in many organisations today is not up to fundamental standards, and the rigours of transformation necessitate considerably higher data quality and analytics. Understanding new types of unstructured data, massive amounts of data from outside your company, leveraging proprietary data, and integrating everything almost certainly entails understanding new types of unstructured data that have never been used.
Data offers an intriguing paradox: most businesses understand the importance of data and the importance of quality, but often squander significant resources by failing to establish the right roles and responsibilities. They frequently blame their IT departments for all of these failures.
As with technology, you need data talent with both breadth and depth. Even more essential is the capacity to persuade significant numbers of front-line employees to take on new roles as data consumers and data providers. This entails considering and presenting the data they require today as well as the data they will require the following transformation.
It also entails assisting front-line personnel in improving their work procedures and duties so that data is generated appropriately.
-
Process
Transformation necessitates an end-to-end mentality, a rethinking of how to fulfil customer demands, seamless integration of work processes, and the capacity to manage across silos in the future. A process approach is a perfect fit for these requirements. However, many people have found it challenging to combine process management horizontally, across silos, and focused on customers with old hierarchical thinking. As a result, this strong notion has become dormant.
Without it, transformation is limited to a series of incremental advances that are essential and beneficial but do not genuinely transform. Look for the ability to “herd cats” aligning silos in the direction of the customer to improve existing processes and design new ones, and a strategic sense to know when incremental process improvement is sufficient and when radical process reengineering is required when building talent in this domain.
-
Change Capacity
We include leadership, teamwork, bravery, emotional intelligence, and other aspects of change management in this area. Fortunately, much has been published on this topic for many years, so we won’t go over it again here, save to say that anyone in charge of digital transformation must be well-versed in the subject.
While we don’t have hard proof to back this up, it appears that people who lean toward technology, statistics, and procedure are less inclined to embrace the human aspect of change.
Areas Of Digital Transformation Initiatives
These are the major areas of digital transformation:
-
Business Activities
Marketing, operations, human resources, administration, customer service, and so on are examples of business activities/functions.
-
Business Processes
One or more interconnected operations, activities, and sets that work together to achieve a given business goal, in which business process management, business process optimization, and business process automation play a role (with new technologies such as robotic process automation).
Today, most sectors and businesses include a mix of customer-facing and internal goals, thus business process optimization is critical in digital transformation plans.
-
Business Models
Business models describe how a company operates, from its go-to-market strategy and value proposition to how it seeks to make money and effectively transforms its core business, tapping into novel revenue sources and approaches, and sometimes even dropping the traditional core business after a while.
-
Business Ecosystems
Firm ecosystems include the networks of partners and stakeholders, as well as contextual variables impacting the business, such as legal or economic goals and changes. On the fabric of digital transformation and information, new ecosystems are being formed between firms with diverse backgrounds, where data and actionable insight become innovation assets.
-
Business Asset Management
Business asset management: the focus is on traditional assets, but increasingly on less ‘tangible’ assets such as information and customers. Customers and information must be considered as genuine assets from every angle.
-
Organizational Culture
Organizational culture, in which there must be a clear customer-centric, agile, and hyper-aware aim, which is attained by developing core skills across the board in areas such as digital maturity, leadership, knowledge worker silos, and so on, allowing the organisation to be more future-proof.
Processes, business activities, collaboration, and the IT side of digital transformation all intersect with culture. Changes are necessary to get applications to market faster. Change is also necessary to make IT and OT operate together in businesses/processes/activities.
-
Partnership Models
Ecosystem and partnership models are evolving, with a surge in co-operative, collaborative, co-creating, and, last but not least, totally new business ecosystem methods, resulting in new business models and income streams. Ecosystems will be critical to the success of the as-a-service economy and digital transformation.
Approaches from customers, employees, and partners People and strategy come first in digital change. Any stakeholder’s shifting behaviour, expectations, and requirements are critical.
-
Partner Approach
This is manifested in several transformation subprojects in which customer-centricity, user experience, worker empowerment, new workplace models, shifting channel partner relationships, and so on (may) all play a role. It is critical to highlight that digital technologies are never the only solution to any of these human issues, from worker happiness to customer experience enhancement.
In the first place, individuals involve, respect, and empower others; technology is an extra facilitator and part of the equation of choice and essential requirements.
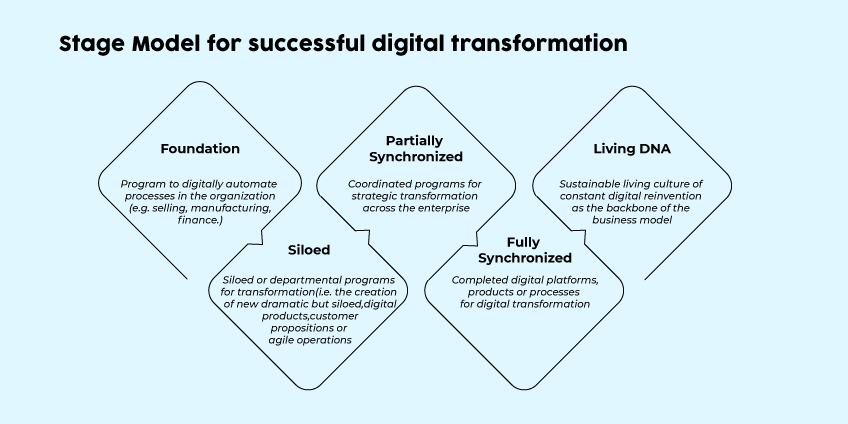
5 Stages Of Successful Digital Transformation Technologies
Now you know what is digital business transformation, and its major functioning areas. So, let us see the digital transformation strategy:
-
Building The Foundation
Digital transformation must begin with laying the proper groundwork, which includes digitising assets and embracing digitalization. Companies at this level are attempting to automate internal operations through the use of software, such as HubSpot or Salesforce as the company’s CRM.
-
Siloed
The next step is when specific functions or departments begin to use technology to optimise operations or to test previously undiscovered business strategies. For example, your Customer Support department may begin utilising a new tool to assess customer happiness, or your Finance department may begin adopting new fintech solutions to ease foreign transactions.
Such modifications, however, are now restricted to specific business units. As a result, they have no impact on the overall firm, and each department may continue to operate independently.
-
Partial Synchronization
Companies reach this point once the C-suite decides to usher the entire firm into the digital era. This indicates that multiple departments or internal procedures are run in a unified fashion. A cross-organizational plan must be created to prescribe the standards that all business units must follow for digital transformation to extend to all divisions.
Regardless of these efforts, no one framework or playbook defines what digital transformation involves for the company. At this level, the previously described culture of experimentation and continual development is also missing.
-
Full Synchronization
Stage 4 is reached when the digital transformation has permeated the company’s DNA and all departmental rules are in place. Nonetheless, the task is not finished. Stage 4 is analogous to putting a new employee on trial – the process can only be completed after it has become an important, stable component of the organisation.
-
Living DNA
The last step in Saldanha’s approach is when a company integrates a digital transformation plan into its entire business strategy. This includes the company’s processes, tools, and skills for identifying risks and opportunities for disruption and responding to them in a disciplined manner consistently.
Digital Transformation: A Transformative Journey Towards Digital Competency
The development of social media has altered service in the same way that it has altered advertising, marketing, and even sales and customer service. Progressive businesses see social media as an opportunity to broaden their service offerings by meeting clients on their preferred channels. So you must implement a digital transformation strategy for absolute success.
We hope this article on what is digital transformation strategy helped you!



