
Discussions over UX and UI definitions have been taking place practically as long as the terminology exists. UX is user experience while UI is the user interface. It is typical for people to swap or occasionally erroneously utilize these terminologies. So, for choosing the correct career path, you must be aware of what is UI/UX design.
If you are confused about UX UI designing, then we got you covered. Today we will be discussing UX vs UI design with UI/UX design examples. In the end, you will get to know everything about UI/UX designer skills, and choose the best career option for yourself.
First Things First: What Is UI Design?
The user interface is the ‘UI’ in UI design. The graphical layout of a program is a user interface. This encompasses the controls you are clicking on, the words you are reading, the images, and all other items through which you communicate. This encompasses the structure of the displays, transitions, animation interfaces, and any micro-interaction.
You determine how the application will appear. They must pick the width of lines and typefaces for text, color schemes, and button designs. UI designers develop an app user interface appearance and feel. Graphic designers are UIs.
Now let us proceed to the next section of our article on User Interface vs User Experience by looking at the brief history of UI design.
-
Brief History Of UI Design
You needed to utilize the command-line interface in the 1970s if you wanted to use a computer. There were no commercial graphical interfaces utilized today. Users need to interact via a programming language for a computer to operate, and endless lines of code were required to do a basic operation.
In the 1980s, computer scientists at Xerox PARC developed the first graphical user interface (GUI). By introducing visual orders using icons, buttons, menus, and checkboxes, people may now interact with their personal computers through this innovative invention. This technological change meant that anybody could use a computer without coding and the personal computer revolution started.
By 1984, Apple Computer launched the Macintosh PC with a point and a mouse click. This sort of interface was first successfully commercially used by the Macintosh personal computer. The accessibility and frequency of personal – and business – computers meant that user-friendly interfaces had to be created.
They wouldn’t sell if they couldn’t engage with their computers. This led to the birth of the UI designer. As with any expanding technology, the work of the UI designer has changed as gadgets require more and more systems, preferences, and accessibility. Now UI developers are not just working on computer interfaces, but mobile phones increased virtual reality, and even “invisible” or screenless interfaces such as speech, gesture, and light.
The UI designer nowadays has almost endless possibilities of working on websites, mobile apps, wearable technologies, and smart home gadgets. It is now important to create interfaces that can be used effectively by people of different ages, backgrounds, and technological expertise.
-
Process Of UI Design
There is little to no difference between UX UI design process. But for being on the safe side, let us give you a thorough walkthrough of the UI design process:
- Research: This step comprises the identification of the target audience and investigation of the design problems and scope.
- Design: The designer produces in this stage an ultimate layout design, with the choice of the proper interface components, such as buttons, icons, sliders, scrollbars, appealing color themes, correct font design, optimized pictures, and structured navigation.
- Testing: This involves testing usability, identifying error areas, finding solutions for the corresponding error areas.
Now, What Does UX Stand For?
“UX” means “user experience”. The experience of a user with the app depends on how they interact. Good UX design ensures a seamless, straightforward user experience instead of perplexing and confused. It also demands a logical rather than random navigation architecture.
Interacting with the app should offer consumers the sensation that they do their work effectively instead of feeling like a fight. User experience depends on how much the user interface elements generated by the user interface are easy or complicated to interact with. Therefore, UX developers are equally concerned with the UI of an application, which is why the distinction between the two is misunderstood.
However, whereas UI designers have to decide how the user interface looks, UX designers are responsible for defining how the UI works. The interface structure and functionality are determined. How structured it is and how everything is interconnected. Briefly, the interface is how it works. It is vital for UX designers how consumers want to engage with their applications is fully understood.
-
Key Factors That A UX Designer Must Know
7 key factors affect the user’s experience. These key factors are related to each other, and every good UX designer should follow these rules:
- Usefulness: Companies must supply customers with valuable products or services. Nobody wants to waste their time on a product or service that does not easily enable their objectives to be achieved.
- Usability: Usability means how consumers can achieve their goals with a product quickly and efficiently.
- Findability: Finding the product easily. All aspects need to be user-friendly in web design.
- Credibility: The customer’s confidence in your goods is called. Customer feedback and reviews on your website contribute to trustworthiness.
- Desirability: When the user has several alternatives, desirability plays a key role. Wishing establishes an emotional connection with the user. For keeping consumers, a pleasant user experience is essential.
- Accessibility: All types of users should access your product, including those with different forms of handicaps like hearing loss, visual impairment, etc.
- Valuable: The product should provide the user with value.

-
Process Of UX Design
As we mentioned earlier, there is not a major difference between UI and UX design processes. So, let us see the minor changes that differentiate the UX design process from the UI design process:
- Research: You will attempt at this phase to grasp the demands of the user, conduct customers, and the analysis of the rival. This allows you to build user individuals and generate experiential maps.
- Design: The functionality and features of this phase are defined. UX designer develops basic design based on the collected data. This phase often involves drawing paper drawings, creating wireframes, creating sitemaps, and prototyping.
- Validation: The designer conducts a usability examination in the validation stage, to determine whether the product was developed during the design phase. The procedure continues until client satisfaction is achieved.
With this section, we conclude the basic introduction of UI and UX design. Now let us see the UI UX designer skills.
What Is A UI Designer & What It Does?
You may want to be more interested in UI design if you appreciate the concept of creating great user experiences but view yourself as a more visual person. Below is a quick overview of the major duties of the UI designer:
1. Product Appearance And Feel
- Client Analysis
- Research On Design
- Branding & Graphic Design
- Guides For User Stories
2. Interactivity And Responsiveness
- Prototype Of UI
- Animation And Interactivity
- Fit Every Screen Sizes
- Developer Implementation
The UI role is important for any digital interface as a visual and interactive designer, and a fundamental aspect for clients to trust a brand. While the brand itself never lies exclusively with the UI designer, it is translated into the product. There is also the endpoint, which indicates that a developer has a duty for “implementing” the design.
Although usually, this is how UI professions have worked in the past, it’s important to know that lines blurred when the word web designer is substituted by user interface creators’ know-how. While UX does not involve code, UI is an element of developing interactive interfaces which, as time advances, depend on it.
What Is A UX Designer & What It Does?
How do UI designers translate into everyday tasks? In short, what function does the UX developer play?
1. Content Strategy
- Analysis Of The Competition
- Analysis Of Clients And Users
- Structure And Strategy Of The Product
- Development Of Content
2. Prototyping & Wireframing
- Testing And Processing
- Planning For Development
3. Execution & Analytics
- UI Designer Coordination
- Developer Coordination
- Tracking And Integration Objectives
- Iteration And Analysis
This means part marketer, part designer, and project manager; the position of UX is difficult, tough, and multifaceted. UX is complex. You can see that this product is referred to twice in connection with analysis or testing, but in fact, you would put it between all other items on the list. Ultimately, the objective is to link corporate objectives with user demands using a testing and perfecting process to achieve the results of the connection on both sides.
So, this was all about UX UI designer skills. You can understand the difference between both of their soft skills by the graphic illustrated below:


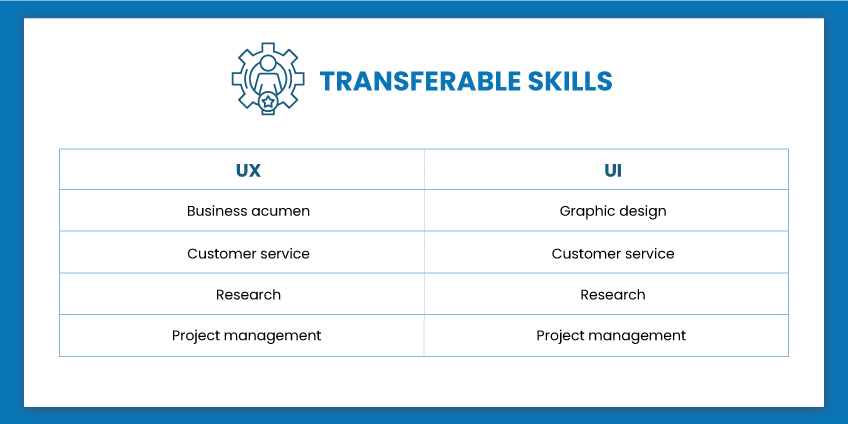
UX Design Vs. UI Design: Major Differences
Despite so many similarities that UI and UX have, they have few major differences. So, let’s check them out:
1. Different Focus
The main distinction between the user interface and UX designers is that they employ prototypes differently. A prototype should be a hi-fi model for many IT designers. For the UX designer, though, loyalty is an afterthought; rationality is more important to them. Just to put it simply, show them the design produced by the UI designer when you meet your consumers. Take the prototype of the UX designer when you meet the coders.
2. Different Color Palettes
Designers of UIs tend to build full-color prototypes. In contrast, in prototypes design, UX designers typically just utilize 3 colors: black, white, and grey. In the design and use of icons, this distinction is often apparent.
For example, if you require a lower navigation bar, UI designers will put as much work into producing it as feasible, even before and after clicking, using the color of the button. Instead, UX designers insert the correct button and write a message after pressing grey.
3. Different Tools
As the tasks of UI and UX designers vary greatly, the tools they are using need to be distinct from each other. The design of pictures is of paramount importance for UI designers. Tools like Flinto and Principle are therefore beneficial, which are tied to Sketch. InVision is an alternative as well and is made competitive by the team collaboration function.
A wireline is preferred by UX designers as it saves time and improves the design. Mockplus with its simple and transparent functioning, Balsamiq with a sketch style, and Axure with extensive capabilities are all experts in prototyping.
4. Look & Feel
UX design primarily addresses the user’s product or service expectations. UX’s ultimate objective is to find and address consumer issues. From another point of view, UI design simulates what UX designers develop behind the scenes. Building on practical needs, UI builds the product interface and uses theories, standards, and aesthetics to provide a world-class onscreen experience.
5. User Journey & Product Snapshot
The backbone of UX is your audience. The main aim of UX research, testing, and experimentation is to understand and improve user experience. Conduct, functional interaction, and emotional reactions are the cornerstone for UX strategies of a firm throughout the user experience.
UI designers, on the other hand, focus on customer love design to encourage consumers to do their UX staff intended measures. UI designers integrate the finest possible layout with graphics, interactivity, motion, and branding. They must convert conceptual information and layout into a user interface that is beautiful, intuitive, and responsive.

UX Design & UI Design: Art Of Harmony
Continued communication and cooperation between UI and UX designers help to ensure that the final user interface appears as efficient and intuitive as possible. Despite their differences, UI and UX work together to achieve a single goal in the most efficient manner.
-
Research Is Most Vital Key
For UI and UX designers, research is important. The two disciplines need to collect as much information as possible to support them in the creation of suitable designs. Both are going to investigate what people desire. What people expect from apps of this kind. This research frequently involves usability sessions, when actual users interact with scaled copies of specific features or visual designs that are examined to identify whether designers are heading in the right direction.
Each iteration includes feedback. To measure the user’s responses to the testing capability, it is necessary to generate lower-fidelity prototypes such as the wireframe renderers of interface components.
-
Creativity Is The Mantra To Success
UX and UI are ideas that are interconnected and complementary. UX designers spend much time analyzing the conduct of the user to create an effective experience. UI designers, on the other hand, work on a wireframe-based visible portion.
-
User’s Empathy Is Top-Priority
Your design may appear great without UX, but it can’t work. Note that a website that looks excellent isn’t enough to boost conversion. It indicates that your design is fine, but it doesn’t seem attractive. UI design supports users in building a personal connection.
UI And UX: Two Different Faces Of The Same Coin
Despite these variations, the user experience and design of the user interface go together. You may find out what consumers value and transform it into value for your firm through research, measurement, and experimenting. Together, UX and UI may increase customer happiness and user experience while growing the number of users in return.
For the success and expansion of your project, strong branding with intuitive UX and UI is the definite need of the hour.



