
The role of redirects is very simple. Using a 302 redirect when you transfer it temporarily. But maybe you ask, why does that matter? After all, the distinction of 301 vs 302 redirect cannot be seen by users.
301 vs 302 redirect work in the same way. The response is simple: the 301 views and 302 redirect view of the search engines differently. And the mistake can cause SEO problems that sometimes go unknown for months or even years. In this article, we will be discussing 301 vs 302 redirect in detail, where to use them, and how to use them efficiently:
What Is A Temporary Redirect?
A temporary redirect is an automatic transmission from one URL to a different URL on the server or client-side. The redirects are used for different purposes, such as moving a website to a new domain, sending traffic temporarily during server maintenance, mixing redundant material, and moving visitors to new sites from old content parts out of date.
Types Of Permanent Redirect
- 301 Redirect
- 302 Redirect
- Meta Refresh
Now let us see the 301 vs 302 redirect definition:
What Is A 301 Redirect?
A 301 redirect code sends the search engine notification that a website or page has been permanently relocated. Continuous means for a year or more. After one year, search to see if you still have users on your site. If so, find out where you come from and try to correct the source before the redirect is canceled. 301 redirect code is also called moved permanently redirect.
What Is A 302 Redirect?
A status code 302 redirect means found, or better known as “temporarily relocated.” This transmission does not contain or transfer the meaning of the connection to the new site. It does make sure that the user is not viewing an incomplete connection, a page 404 that is not found, or an error page at a suitable location. 302 redirect means moved temporarily.
What Is Meta Refresh?
Meta refreshes are a kind of page-level redirection instead of a server-level redirect. They are typically slower and SEO is not suggested. Although meta refreshes pass some link equity, it is not recommended as an SEO strategy because of the poor usability and loss of link shares.
When To Use 301 Redirects?
Many people are using such 301 redirects to buy domains they want (brand misspelling, brand variations, or related domains with a “domain authority”) to their primary domain. It is also useful to use a 301 to set your default domain: “www.your website.com” or “your website.com.”
When people write or type website names, they prefer to leave the “www” out, so permanent redirects guarantee that they end up on your site even if they do not type “www.” In this world of effective digital marketing strategies, knowing 301 redirects is a must.
When To Use 302 Redirect?
If you want to send visitors to a new site or page for a short time like redesigning or upgrading your website, you can use this form of redirect.
Only if you plan to return the old page can you use a 302. If you want to test a new page and get some reviews from consumers, without injuring their rankings from the original one, you might also use a 302 redirect.
You will ask, “Why would I use it then if it doesn’t offer SEO value?” A good example of how to redirect a 302 redirect is in an e-commerce setting. Say you have a product you don’t have for sale anymore – it could be seasonal, out of stock, or something you might sell again. You will want to return the user to the page category using a 302 redirect.
If the product failure happens for a real duration, it might be unreasonable to forward the customer to a page they cannot order from, so you can refer them to the category page for similar products. And with that 302 redirect you tell the crawlers that your story is your story.
And with the 302 redirect you tell search engine crawlers that your content is temporarily offline and that the page’s value is not to be moved to another URL. It is necessary to keep technical signals in mind as you approach your SEO and alter the location or layout of your site. Incorrect usage could trigger a devastating loss of your content’s connection value, which could be difficult to resolve or reconstruct.
How Google Treats 301 Vs 302 Redirect
Since the functionality for 301 redirects and 302 redirect is the same as for the end-user, it’s mainly up to Google to select which one to use. And here we must talk about two things:
- Indexation
- Links
1. Indexation Of 301 Vs. 302 Redirect
Google can only index one of these URLs when a URL is forwarded to another.
a) For 301 Redirects
Google can index new-page.html and de-index old-page.html if you create a 301 redirection from old-page.html to new-page.html. That is because the 301 redirect code says it is a continuous step for Google so that it doesn’t make any point to index the old URL.
Often people get confused because the old URL will still appear for a while in Google with searches after the creation of a 301 redirect code.
b) For 302 Redirect
URL typically the original one that Google indexes. Since Google knows that people use 302 redirect sometimes incorrectly for permanent redirects, they test each 302 redirect one by the other to try to find out what you said.
Nobody knows exactly how much time a 302 redirect must be in place before Google starts to process it as a permanent redirect. It’s usually a few weeks to a couple of months, but it may be days, weeks, or months.
Google tends to treat 302 redirect as 301 redirects from the go under some conditions. When Google crawled into the ‘old’ domain and saw the redirection, the ‘old’ domain was lost to the ‘new’ domain.
Only search the last date of crawl if you do. If this date comes after the redirect is introduced, re-index and return later.
2. Links
Now, if you redirect one URL to another, you merge link signals on one URL without dilution. However, it is widely misunderstood how this works, because the method of transmission will affect the consolidation of signals.
a) For 301 Redirects
Signals about the ‘latest’ URL consolidate ‘forward.’ For instance, if you use old page.html to redirect (301) backlinks, you can merge all connection signals on the new page.html. In other words, New-page.html should be ranked by Google like it has 10 connections.
If you transfer content to a new URL without altering it dramatically, there is no problem. But if the redirect is meaningless, as the case in the redirection to your homepage of an old blog post, it is probably not useful to have links to the ‘old’ page. The golden rule, therefore, remains as relevant as possible for your redirects.
If you’re curious about how Google treats one of your 301, try: Go to Console for Search > Links > External Links.
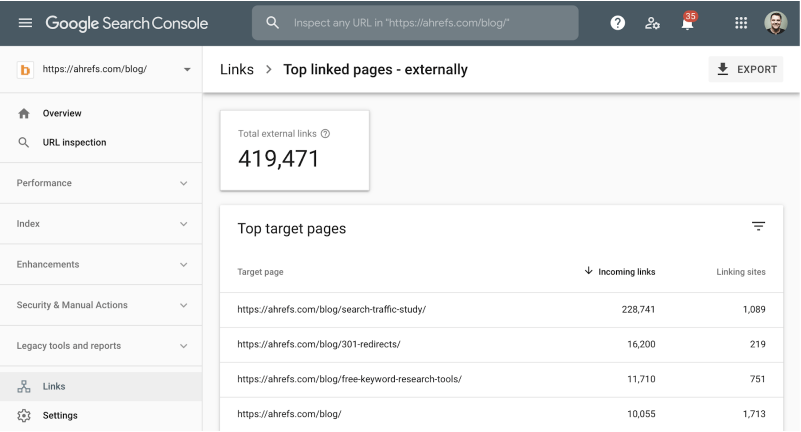
Next, filter the “Goal Page” report and press the ‘New’ URL. Then insert the ‘old’ URL into the web Explorer of Ahrefs and go to the report for referring the domains. Finally, filter the links by “Site” in the GSC and paste them one by one.
Google probably treats the redirect as softens 404 and doesn’t count the backlinks for the ‘fresh’ URL if you do this for multiple referencing domains and don’t get matches in GSC. Note that the ‘Target URL’ column (if different) displays the ‘old’ URL. This tells us that the redirected URL to the new URL is counted by Google.
b) For 302 Redirect
The ‘backward’ to ‘old’ URL normally consolidate link signals. When, for example, 302 redirect old-page.html is redirected to the new-page.html, and new-page.html includes ten backlinks, all link signals are normally consolidated on old-page.html. This means that Google should classify old-page.html as having 10 links.
But things aren’t that straightforward. It depends on how the 302 redirect is handled by Google. If you regard it as a provisional redirect, the signals of communication will consolidate backward. This is supposed to be the same or identical to the new page. the redirected page is. If not, it can be considered as a 301 moved permanently.
If you consider the link signals 301 moved permanently as a continuous redirect, they will consolidate
How Do 301 Vs 302 Redirect Impacts SEO
Using 301 redirects, Google removes the old page from its index and transfers the most value from it to the new page. In so doing, you must not ignore the need of search engines for the transition and see any possible impact/change in rankings as you switch a site from one URL to another.
A 302 redirect is not detrimental to your SEO efforts when used properly. The original page is indexed in Google and the value (link stock) isn’t changed to the new URL when you select this form of redirection, because Google knows this is only temporary. You will then maintain any rankings, traffic importance, and authority on that link.
If people don’t know how the discrepancies between the two appear to increase issues, they select a 302 place to permanently redirect it. They create a new website or page and do not pass the value they have gained over time. That is why the difference between 301 redirects and 302 redirect is necessary to understand and whether both are suitable.
Best SEO Practices For 301 Vs 302 Redirect
Typically one URL is routed to a different one. To preserve SEO value, it is essential to follow best practices. The first popular example is a simple case, a URL that needs to be permanently redirected to a different address.
There are many alternatives, but the 301 redirects are generally preferred for users as well as search engines. The 301 service means that the website has been relocated indefinitely for both browsers and search engine bots. This is interpreted by search engines as not only changing the position of the website but also finding the content or a modified version at the new URL.
Any link weighing from the first page to the new URL will be carried by the engines as follows:
- Notice that the search engines are taking some time to find the 501, identify it, and create the new page with the ranking and confidence of its predecessor while shifting a page from one URL to another. If you don’t visit this website rarely, or if the new URL doesn’t correctly resolve, this procedure will take longer than that.
- Other redirection alternatives, such as meta refresher, maybe bad replacements because they cannot pass the rankings as accurately and search engine values as a 301 redirect code would.
- The transition of content is made more complicated by changing the domain of an entire website or by transferring content from one domain to another. Owing to the harassment of spammers and the distrust of the search engines, often 301 redirects and 302 redirect between domains take longer to spin and count properly.
How To Do 301 Redirects & 302 Redirect
You need to access the .htaccess file of your server to “implement 301 redirects to websites hosted in servers running Apache.” They have an Apache Tutorial and a URL Rewrite Guide if you aren’t certain how to do that. You need to ask your host for direction if your server does not run with Apache.
If your site uses WordPress, you can render redirection as simple as possible using the following plugins. Certain useful plugins are:
- Redirect
- Redirects Simple
- SEO Redirector
Final Takeaway
Redirects aren’t confusing. This is not. Use a redirect 301 redirects if you permanently transfer content to a new site. Using a 302 redirect if you switch it temporarily. However, it might be comforting to know that even though you use the incorrect kind of redirect, Google would probably find out what you ultimately said.
Does that ever occur? Naturally not. Google is not always intelligent enough to always find out what you intended without error, so it is good practice to redirect as often as possible with the correct form. Get up on the variations and ensure that you use the right direction for the right result.
When using a 302 redirect that is expected to be temporary and later finds that a permanent change will occur, make sure that you change the redirection between a 302 redirect and 301 redirects. Finally, check your rankings so that Google can index your new pages without making any mistakes that could lead to your ranking. If you want to take assist from the most trusted digital marketing agency, then feel free to contact us.



